Time limit: 0
Quiz Summary
0 of 37 Questions completed
Questions:
Information
You have already completed the quiz before. Hence you can not start it again.
Quiz is loading…
You must sign in or sign up to start the quiz.
You must first complete the following:
Results
Quiz complete. Results are being recorded.
Results
0 of 37 Questions answered correctly
Your time:
Time has elapsed
You have reached 0 of 0 point(s), (0)
Earned Point(s): 0 of 0, (0)
0 Essay(s) Pending (Possible Point(s): 0)
| Average score |
|
| Your score |
|
Categories
- Not categorized 0%
- NBME 7 BLOCK 4 0%
Would you like to submit your quiz result to the leaderboard?
![captcha]()
Loading
| Pos. | Name | Entered on | Points | Result |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Table is loading | ||||
| No data available | ||||
- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
- 15
- 16
- 17
- 18
- 19
- 20
- 21
- 22
- 23
- 24
- 25
- 26
- 27
- 28
- 29
- 30
- 31
- 32
- 33
- 34
- 35
- 36
- 37
- Current
- Review
- Answered
- Correct
- Incorrect
-
Question 1 of 37
1. Question
A 42-year-old man with a long history of type 1 diabetes mellitus comes to the office due to frequent involuntary loss of urine. For the past several months, he has been having difficulty starting and maintaining a urinary stream. In the last 3 weeks, he has had 2 episodes of nocturnal enuresis and multiple daytime episodes of uncontrolled voiding without any sensation of a full bladder. His other medical problems include chronic kidney disease and gastroparesis. He does not use tobacco or alcohol. Which of the following additional findings would most likely be present in this patient?
CorrectIncorrect -
Question 2 of 37
2. Question
An apparently healthy 6-year-old boy is enrolled in a research study designed to assess the absorptive capacity of the small intestine. As part of the investigation, he is administered an oral solution containing free amino acids and amino acid derivatives. Blood samples are then obtained at 15-minute intervals for the next 2 hours. The patient is found to have significantly decreased intestinal absorption of lysine, arginine, ornithine, and cystine as compared to the other study participants. If the condition is left untreated, which of the following complications is this patient at greatest risk of developing?
CorrectIncorrect -
Question 3 of 37
3. Question
A 45-year-old man comes to the office for an annual medical visit. The patient has had prediabetes for the last 2 years. He feels well and takes no medications but has gained weight since his last visit a year ago. The patient has a strong family history of type 2 diabetes mellitus. Blood pressure is 124/78 mm Hg and BMI is 32 kg/m2. Laboratory results show a fasting blood glucose of 157 mg/dL and serum creatinine of 0.7 mg/dL. Hemoglobin A1c is 7.4%. Urine assay shows no detectable albuminuria. Which of the following renal changes is most likely present in this patient at this time?
CorrectIncorrect -
Question 4 of 37
4. Question
A 34-year-old woman comes to the hospital with a 4-day history of abdominal cramps, nausea, and watery diarrhea. Today she developed dizziness on standing. Her child has had similar symptoms recently. The patient has no prior medical conditions and takes no medications on a regular basis. Blood pressure is 124/82 mm Hg while supine and 100/70 on standing; pulse is 98/min. Examination shows dry mucous membranes. The abdomen is soft and nontender. Laboratory results are as follows:
Serum chemistry
Sodium
144 mEq/L
Blood urea nitrogen
50 mg/dL
Creatinine
1.8 mg/dL
Urinalysis
Protein
negative
Red blood cells
0/hpf
White blood cells
0-1/hpf
Microscopy
few hyaline casts
Urine sodium
8 mEq/L
Which of the following changes are most likely to be seen in this patient?
 CorrectIncorrect
CorrectIncorrect -
Question 5 of 37
5. Question
A 52-year-old postmenopausal woman comes to the office due to urine leakage with coughing and sneezing. She has no dysuria, urgency, or changes in urinary frequency. The patient has had 3 spontaneous vaginal deliveries. On pelvic examination, there is mild vulvovaginal atrophy and anterior vaginal wall prolapse. The remainder of the physical examination is normal. The patient is advised to perform exercises to strengthen her pelvic floor as part of treatment for her symptoms. Which of the following structures is the most likely target of the exercise?
CorrectIncorrect -
Question 6 of 37
6. Question
A 37-year-old woman, gravida 2 para 1, at 28 weeks gestation comes to the office due to leakage of urine. The patient has had intermittent leakage with cough but no dysuria or hematuria. She reports normal fetal movement and has had an uncomplicated pregnancy. Four years ago, the patient had a spontaneous vaginal delivery of a 3500 g (7 lb 11 oz) neonate. The patient has no chronic medical conditions or prior surgeries. Vital signs are normal. Prepregnancy BMI was 32 kg/m2. She has gained 15.8 kg (34.8 lb) during this pregnancy. The abdomen is gravid, and there is no suprapubic tenderness. Urinalysis is negative for blood, leukocyte esterase, and nitrite. Which of the following is the most likely mechanism for this patient’s urinary incontinence?
CorrectIncorrect -
Question 7 of 37
7. Question
An 86-year-old man is hospitalized for a complicated hip fracture requiring surgical repair following a fall. His medical problems include prostate cancer, gout, and osteoarthritis. An indwelling urinary catheter is placed due to initial urinary retention and immobilization following the surgery. On the eighth day of hospitalization, the patient develops fever and altered mental status. After evaluation and laboratory testing, a urinary tract infection is diagnosed. Which of the following is the most effective strategy for preventing this complication?
CorrectIncorrect -
Question 8 of 37
8. Question
A 73-year-old man comes to the office due to blood in his urine. He has noted bright red blood at the end of micturition on several occasions but has had no urinary frequency or pain with urination. The patient has a history of hypertension and chronic bronchitis. He has smoked a pack of cigarettes daily for 30 years. Temperature is 37 C (98.6 F). Abdominal, external genital, and rectal examinations are unremarkable. Urinalysis shows hematuria. Urine cytology is positive for malignant cells. Cystoscopy is planned for visualization and biopsy of suspected urinary tract cancer. Which of the following features would be most suggestive of a poor prognosis?
CorrectIncorrect -
Question 9 of 37
9. Question
A 60-year-old man comes to the office due to dark, rusty-colored urine for the last 2 weeks. He reports no pain, urinary frequency, or urgency. The patient has no chronic medical conditions and takes no medications. He smoked a half pack of cigarettes daily for 10 years but quit 30 years ago. His father had hypertension and his mother has Alzheimer dementia. Urinalysis shows a large number of red blood cells. Renal ultrasound reveals a mass in the right kidney. Cytologic evaluation of the mass shows malignant cells with a chromosome 3p deletion. The deletion most likely involves which of the following genes?
CorrectIncorrect -
Question 10 of 37
10. Question
A 55-year-old woman comes to the office due to swelling around her ankles and face that has progressively worsened over the last 1-2 months. The patient has 2+ bilateral pitting edema in the lower extremities, trace edema in the upper extremities, and periorbital edema. Cardiopulmonary examination is normal. Laboratory evaluation shows a serum creatinine level of 2.0 mg/dL and an albumin level of 2.8 g/dL. Urinalysis shows 3+ proteinuria and no hematuria or casts. A kidney biopsy is performed; light microscopic findings following staining with hematoxylin and eosin are shown in the image below:

Which of the following is the most likely explanation for this patient’s biopsy findings?
CorrectIncorrect -
Question 11 of 37
11. Question
A 65-year-old hospitalized man is evaluated for decreased urine output and increased serum creatinine. The patient was admitted for 3-vessel coronary artery disease and underwent coronary artery bypass grafting surgery yesterday. Other medical conditions include type 2 diabetes mellitus and hypertension. He received a dose of intravenous vancomycin prior to the surgery for prophylaxis of surgical infection. The patient has also been receiving 100 mL/hour of intravenous normal saline for the past 24 hours. He is afebrile. Blood pressure is 130/80 mm Hg and pulse is 80/min. Examination shows bibasilar crackles. The abdomen is soft. Urine output over the past 6 hours is 100 mL. Laboratory results are as follows:
Day of admission
Today
Blood urea nitrogen
20 mg/dL
35 mg/dL
Serum creatinine
1.3 mg/dL
2.5 mg/dL
Urine sediment microscopy is shown in the exhibit. Which of the following is the most likely cause of this patient’s current condition?
 CorrectIncorrect
CorrectIncorrect -
Question 12 of 37
12. Question
A 21-year-old woman comes to the office for evaluation of urinary frequency and urgency for the past 2 days. She has also noticed scant vaginal discharge. The patient has never had these symptoms before. She has no chronic medical conditions, and she takes a combination oral contraceptive pill daily. The patient has been sexually active with multiple partners over the last year. She is a college student and does not use tobacco, alcohol, or illicit drugs. A urine sample is obtained for urinalysis and culture. Which of the following additional findings would be most suggestive of a diagnosis of pyelonephritis?
CorrectIncorrect -
Question 13 of 37
13. Question
A 17-year-old boy is brought to the office due to occasional blood in the urine. The first episode occurred 1 year ago during a flulike illness, and resolved spontaneously. The patient had a similar episode about 6 months ago, which also seemed to resolve. He has no other medical conditions and does not use tobacco or alcohol. There is no history of blood or kidney disorders in the family. Vital signs are normal. On laboratory evaluation, blood urea nitrogen level is 14 mg/dL and creatinine is 0.8 mg/dL. Urinalysis results are as follows:
Specific gravity
1.013
Protein
+2
Blood
trace
Glucose
negative
Ketones
negative
Leukocyte esterase
negative
Nitrites
negative
White blood cells
1-2/hpf
Red blood cells
20-30/hpf
A renal biopsy is performed. Which of the following findings is most likely to be seen on microscopic evaluation?
CorrectIncorrect -
Question 14 of 37
14. Question
A 21-year-old male presents to his physician after noticing that his urine had a “frothy” appearance. He also complains of easy fatigability and anorexia. His past medical history is significant only for an upper respiratory infection several weeks ago. Physical examination reveals symmetric pitting edema of the ankles. Which of the following is most likely decreased in this patient?
CorrectIncorrect -
Question 15 of 37
15. Question
A 37-year-old woman comes to the office due to worsening leg swelling for the past 2 months. She has also felt excessively tired and has had achy pain in her hands. Temperature is 37.3 C (99.1 F), blood pressure is 156/92 mm Hg, and pulse is 86/min. BMI is 32 kg/m2. Physical examination shows 2+ pitting bilateral edema in the lower extremities. Bilateral finger joints and wrists are mildly swollen and tender to palpation. Serum creatinine level is 1.8 mg/dL. Urinalysis is positive for proteinuria and hematuria. Light microscopy of samples from a kidney biopsy shows diffuse, global endocapillary hypercellularity. Direct immunofluorescence demonstrates “full-house” staining with diffuse, global, granular staining of glomerular capillary walls by IgG, IgM, IgA, C1q, and C3. Electron microscopy shows abundant subendothelial electron-dense deposits. Which of the following is the most likely underlying cause of this patient’s renal disease?
CorrectIncorrect -
Question 16 of 37
16. Question
A 34-year-old man with type 1 diabetes mellitus comes to the office due to achy pain in the shoulders, elbows, and thighs over the past several months. The patient was diagnosed with diabetes 15 years ago and has had difficulty adequately controlling it. He currently takes multiple daily injections of insulin. Vital signs are within normal limits. Physical examination shows mild pedal edema. Serum creatinine is 2.2 mg/dL, up from 1.6 mg/dL six months ago. Additional laboratory results show low serum calcium and elevated parathyroid hormone levels. Inhibition of which of the following enzymatic steps is most likely responsible for this patient’s current symptoms?
 CorrectIncorrect
CorrectIncorrect -
Question 17 of 37
17. Question
A group of researchers is studying secondary hypertension in porcine models of renal artery stenosis. During an experiment, a clip is placed that constricts the right renal artery to 30% of its original cross-sectional area. A few days later, hemodynamic and biochemical measurements are recorded and compared to measurements obtained before clip placement. Which of the following changes is most likely to be seen in the experimental animals?
CorrectIncorrect -
Question 18 of 37
18. Question
A 26-year-old woman dies shortly after a sudden-onset, severe headache. She was recently diagnosed with hypertension but otherwise had no medical problems. The patient was a lifetime nonsmoker and did not use illicit drugs. Autopsy reveals evidence of intracranial hemorrhage. Both carotid arteries appear tortuous distally with alternating areas of fibrotic webs and aneurysmal dilation. On microscopic examination, the aneurysmal segments of the carotid arteries lack an internal elastic lamina. Which of the following is the most likely additional finding in this patient?
CorrectIncorrect -
Question 19 of 37
19. Question
A 1 week-old boy is evaluated in the hospital. The patient has been admitted due to urosepsis and is receiving antibiotic therapy. The mother received no prenatal care; the neonate was born at term via spontaneous vaginal delivery. Vital signs are normal. Examination shows lower abdominal distension with normal bowel sounds. The penis and scrotum appear normal. Renal ultrasonography and voiding cystourethrography reveal a diffusely thickened bladder wall with bilateral vesicoureteral reflux and hydronephrosis. Which of the following is the most likely cause of this patient’s findings?
CorrectIncorrect -
Question 20 of 37
20. Question
A 32-year-old man with a history of chronic hepatitis B infection is evaluated for generalized edema. Kidney disease is suspected, and renal biopsy is performed. Histologic sections of the kidney show diffuse glomerular hypercellularity and diffuse thickening of the capillary walls. Immunofluorescence demonstrates prominent staining for IgG and C3 with coarse, granular basement membrane and mesangial positivity. Electron microscopy shows extensive subendothelial and mesangial deposits. Which of the following is the most likely diagnosis?
CorrectIncorrect -
Question 21 of 37
21. Question
A 64-year-old man comes to the emergency department due to flank discomfort and red urine. He has a history of hypertension and type 2 diabetes mellitus. Three months ago, the patient had an ischemic stroke and now has mild, residual, right-sided weakness. Serum creatinine is 0.9 mg/dL, and serum lactate dehydrogenase is elevated. Urine microscopy shows many red blood cells. The findings of a CT scan of the abdomen with contrast are shown in the image below:

Which of the following is the most likely cause of this patient’s symptoms?
CorrectIncorrect -
Question 22 of 37
22. Question
A 20-year-old man is brought to the emergency department after being found confused and somnolent in his apartment. His face and upper body are covered with emesis. The patient was last seen with a normal appearance 4 hours ago. Medical history is significant for excessive alcohol use. Temperature is 36.8 C (98.2 F), blood pressure is 120/88 mm Hg, pulse is 102/min, and respirations are 26/min. The patient is barely rousable and does not answer questions. Cardiopulmonary examination is normal. The abdomen is soft and nontender. There are no focal findings on neurologic examination. Laboratory results are as follows:
Serum chemistry
Sodium
136 mEq/L
Chloride
91 mEq/L
Bicarbonate
6 mEq/L
Urea nitrogen
22 mg/dL
Creatinine
1.9 mg/dL
Glucose
80 mg/dL
Lactic acid
normal
Serum osmolality
380 mOsm/kg
Arterial blood gas (on room air)
pH
7.19
PO2
110 mm Hg
PCO2
20 mm Hg
Acute poisoning is suspected and the patient is given an appropriate antidote. Which of the following is the most likely mechanism of action of the antidote?
CorrectIncorrect -
Question 23 of 37
23. Question
Researchers are studying the mechanisms that lead to acute kidney injury in septic shock. In an experiment, the renal perfusion pressure of laboratory mice is reduced to assess changes in renal tubular function and morphology. Perfusion pressure is decreased until renal tubular dysfunction occurs due to sublethal cellular ischemia; recovery of function is achieved within several hours of reperfusion. Which of the following is most likely the earliest change to occur within the renal tubules during the ischemic period?
CorrectIncorrect -
Question 24 of 37
24. Question
A 58-year-old man comes to the emergency room due to headache. Medical history is significant for long-standing hypertension and medication nonadherence. Blood pressure on arrival is 231/135 mm Hg. Twenty minutes after intravenous hydralazine is administered, blood pressure is 145/95 mm Hg. Over the following 24 hours, serum creatinine increases from 1.1 to 1.6 mg/dL. Urine sediment demonstrates abundant granular casts. Which of the following processes best explains this patient’s acute kidney injury?
CorrectIncorrect -
Question 25 of 37
25. Question
A 58-year-old woman comes to the office due to gradually worsening shortness of breath. She has a history of emphysema secondary to alpha-1 antitrypsin deficiency and uses inhaled bronchodilators and glucocorticoids. Lately the patient has been feeling short of breath even with minimal exertion. She has no other medical conditions. The patient is a former smoker with a 5-pack-year history. Blood pressure is 130/80 mm Hg, pulse is 82/min, and respirations are 18/min. Physical examination shows increased anteroposterior chest diameter, prolonged expiratory phase, and decreased breath sounds bilaterally. The heart sounds are distant. Chest x-ray reveals hyperinflated lungs with no consolidation, pleural effusion, or pneumothorax. Which of the following sets of arterial blood gas findings on room air is most likely to be seen in this patient?
 CorrectIncorrect
CorrectIncorrect -
Question 26 of 37
26. Question
A 2-year-old boy is brought to the office due to poor weight gain and frequent urination. His mother says he has not gained any weight since his well child visit 6 months ago, and in the last several months he has been urinating more than 10 times a day. His weight percentile has decreased from 60th percentile to 10th percentile, consistent with failure to thrive. Physical examination reveals frontal bossing. He is found to have glucosuria on urinalysis, although his serum glucose is within normal limits. Additional serum laboratory studies reveal hypophosphatemia, hypokalemia, and a normal anion gap metabolic acidosis. Which of the following structure/function combinations is most likely defective in this patient?
 CorrectIncorrect
CorrectIncorrect -
Question 27 of 37
27. Question
A 65-year-old man comes to the office to establish medical care. The patient states that he was diagnosed with type 2 diabetes mellitus several years ago but has not taken medications or followed up. He reports no symptoms. Blood pressure is 142/86 mm Hg and pulse is 78/min. BMI is 30 kg/m2. Physical examination shows no abnormalities. Laboratory testing shows uncontrolled diabetes mellitus with diabetic nephropathy. He also has findings indicating a decreased aldosterone effect on the renal tubules but no other adrenal or pituitary hormonal disturbances. Compared to healthy individuals, which of the following are most likely in this patient?
 CorrectIncorrect
CorrectIncorrect -
Question 28 of 37
28. Question
A 62-year-old woman comes to the office for medical evaluation. The patient states her 26-year-old son has developed renal failure from chronic glomerulonephritis and is undergoing dialysis therapy. She has the same blood group as her son and she wants to donate one of her kidneys to him. The patient has no chronic medical conditions and takes no medications. Vital signs are within normal limits, and physical examination shows no abnormalities. The patient understands that she may not be a compatible donor based on human leukocyte antigen (HLA) testing. In addition, which of the following age-related renal changes should be taken into consideration when assessing donor suitability?
CorrectIncorrect -
Question 29 of 37
29. Question
A 65-year-old woman comes to the office due to intermittent leakage of urine. For the past 3 months, the patient has had to change her undergarments multiple times a day due to urine leakage. She voids 4 or 5 times during the day and occasionally wakes up at night to void. The patient has type 2 diabetes mellitus and was recently diagnosed with chronic obstructive pulmonary disease after evaluation for a chronic cough. Her only surgeries were 2 cesarean deliveries in her 20s. BMI is 30 kg/m2. Pelvic examination shows leakage of urine from the urethra during the Valsalva maneuver. Postvoid residual volume and urinalysis are normal. Which of the following is the most likely cause of this patient’s clinical presentation?
CorrectIncorrect -
Question 30 of 37
30. Question
A 6-week-old term boy is brought to the office due to increased fussiness and poor weight gain. The patient has several wet diapers per day. His anterior fontanelle is flat and mucous membranes are dry. Laboratory results include the following:
Sodium
148 mEq/L
Potassium
3.5 mEq/L
Antidiuretic hormone
increased
Urinalysis shows a specific gravity of 1.002. Which of the following is the most appropriate treatment for this patient’s condition?
CorrectIncorrect -
Question 31 of 37
31. Question
A 42-year-old man comes to the office due to a 2-week history of reddish-brown urine, fatigue, joint pain, and a lower extremity rash. The patient has no medical history, and family history is unremarkable. He has had multiple sexual partners and only uses protection intermittently. Temperature is 37.7 C (99.9 F), blood pressure is 146/94 mm Hg, and pulse is 75/min. Palpable purpura and pitting edema are present in bilateral lower extremities. Laboratory results are as follows:
Serum chemistry
Creatinine
3.2 mg/dL
Liver function studies
Aspartate aminotransferase (SGOT)
78 U/L
Alanine aminotransferase (SGPT)
96 U/L
Immunologic studies
C3
low
C4
low
Urinalysis
Protein
3+
White blood cells
2-3/hpf
Red blood cells
many/hpf
Casts
several RBC casts
Which of the following immunologic mechanisms is most likely responsible for this patient’s renal injury?
CorrectIncorrect -
Question 32 of 37
32. Question
A 65-year-old man comes to the office with a 2-day history of skin rash and low-grade fever. He has had no cough, shortness of breath, chest pain, vomiting, dysuria, or urinary frequency. The patient was recently diagnosed with acute gouty arthritis and has been taking indomethacin for the past 10 days. Temperature is 38.1 C (100.6 F), blood pressure is 130/90 mm Hg, and pulse is 86/min. Examination shows a diffuse, maculopapular skin rash. Mucosal surfaces are moist without any lesions. Cardiopulmonary examination shows no abnormities. There is no costovertebral angle tenderness. Serum creatinine is 2.3 mg/dL (baseline 1.1 mg/dL, 2 weeks ago). Urinalysis shows numerous white blood cells/hpf. Which of the following is the most likely cause of this patient’s acute renal dysfunction?
CorrectIncorrect -
Question 33 of 37
33. Question
A 16-year-old girl comes to the office due to 2 days of a burning sensation with urination. She had sexual intercourse with her partner last week and used a condom for contraception. The patient says, “I always urinate right after sex.” She has no vaginal discharge, and vital signs are normal. Examination shows suprapubic tenderness. Urinalysis reveals positive nitrites, positive leukocyte esterase, 50 white blood cells/hpf, and many bacteria. Urine β-hCG is negative. Which of the following is the most likely cause of this patient’s infection?
CorrectIncorrect -
Question 34 of 37
34. Question
A 35-year-old pregnant woman at 8 weeks gestation comes to the emergency department due to persistent nausea and vomiting. The patient has had intermittent nausea for the past week and vomiting for the past 3 days. Now, she is unable to tolerate solids or liquids. Temperature is 36.7 C (98 F), blood pressure is 90/64 mm Hg, pulse is 108/min, and respirations are 14/min. Mucous membranes are dry and capillary refill time is delayed. Cardiac examination shows sinus tachycardia and no murmurs. The abdomen is nontender and nondistended. Compared to her baseline, which of the following sets of serum electrolyte concentration abnormalities are most likely present in this patient?
 CorrectIncorrect
CorrectIncorrect -
Question 35 of 37
35. Question
A 55-year-old man is found unresponsive on the street during a cold winter night. He is hypothermic and does not follow commands. Medical history is unavailable. Despite rewarming efforts, the patient dies in the emergency department. An autopsy is performed. Light microscopy of a section of the patient’s kidney is shown on the slide below.

This individual’s renal condition could most likely have been prevented by use of which of the following types of medication?
CorrectIncorrect -
Question 36 of 37
36. Question
A 42-year-old man comes to the office for evaluation of progressive generalized edema and weight gain for the past several weeks. He has no chest pain or shortness of breath. The patient has no chronic medical conditions and takes no medications. He last saw a physician a year ago for an upper respiratory infection. The patient does not use tobacco, alcohol, or illicit drugs. Blood pressure is 130/80 mm Hg and pulse is 84/min. Mild ascites is present. There is bilateral lower extremity pitting edema to the knees.
Laboratory results are as follows:
Serum chemistry
Albumin
2.2 g/dL
Creatinine
1.0 mg/dL
Urinalysis
Blood
negative
Protein
4+
Red blood cells
1-2/hpf
White blood cells
1-2/hpf
Urinary protein excretion is 6.0 g/24 hr. A kidney biopsy is performed, and electron microscopy of a glomerular capillary is shown below:
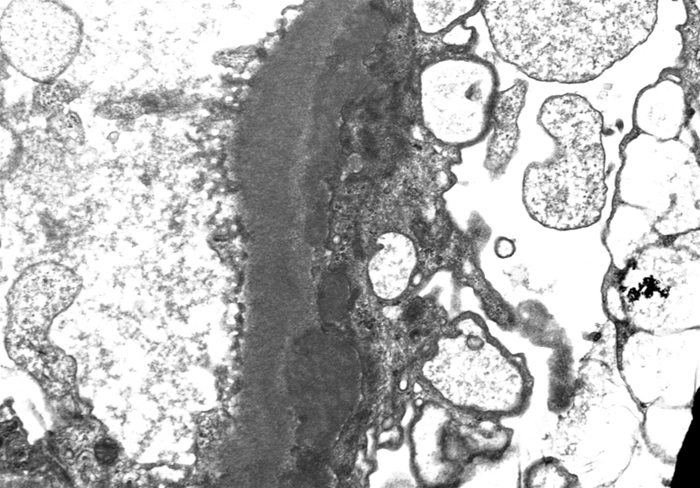
Which of the following is the most likely diagnosis?
CorrectIncorrect -
Question 37 of 37
37. Question
A 55-year-old man is evaluated due to worsening fatigue and exertional shortness of breath. He has no chronic medical conditions and takes no medications. Physical examination shows facial puffiness and bilateral lower extremity edema. Urinalysis shows 3+ proteinuria. Kidney biopsy findings with special staining under polarized light are shown on the image below:

Which of the following tests would be most helpful for establishing a specific diagnosis in this patient?
CorrectIncorrect
